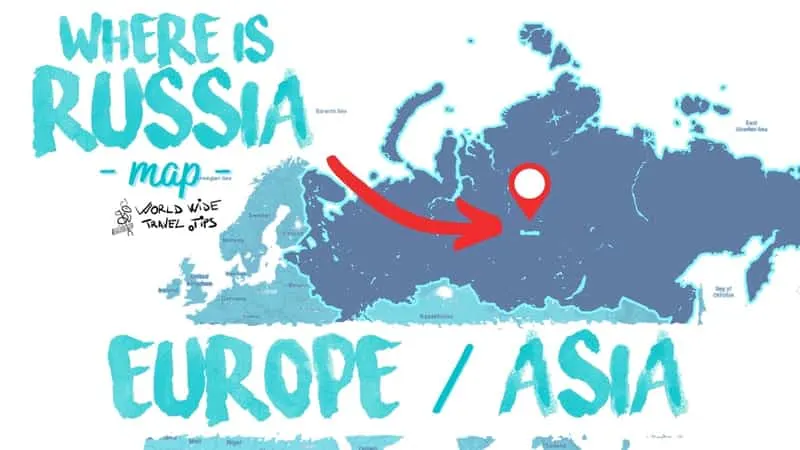
You might be asking yourself where is Russia located in Europe and the exact answer to this question is that it lies in the northeastern part of Europe.
Russia, or the Russian Federation as it is officially known, is a transcontinental country located in both European and Asian continents and is the largest country in the world.
Some of the following links are affiliate links. When you buy something using the retail links in our article, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost for you. You can read our full disclosure disclaimer and privacy policy.
Where is Russia in Europe
Russia covers the northern part of the Eurasian continent with about 75% of its territory being located in Asia and just 25% in Europe.
So, even if it might sound strange, part of Russia is located in Europe, while the other part of the country is in Asia, being one of the very few countries on Earth located on two continents.
The country occupies about 40% of the total surface of the European continent and about 75% of the Russian population lives in the European part.
According to the official records of the United Nations, the natural boundary between the European Russia and the Asian Russia is the Ural Mountain range and the Ural River, Caucasus Mountain and the Turkish Straits.
European Russia or Western Russia as it is also called is located in Eastern Europe on the East European Plain and is bordered by the White Sea, the Barents Sea, the Kara Sea, the Black Sea as well as a large number of bays of the Arctic Ocean.
In the west, the European Russia is bordered by Finland, Norway and Baltic Sea, while in the west it is bordered by Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania.
Other countries which are located right near Russia are Belarus and Ukraine, as well as Poland, Georgia, Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan.
Where is Russia located in Europe and interesting facts
As I said earlier, Europe and Asia are the two continents on which the largest country on Earth which is Russia extends.
As it is so big, the country is split into 21 minority republics, 6 federal territories known as “Krays”, 2 federal cities and here I am talking about Moscow and St Petersburg, 10 autonomous areas and 1 autonomous region.
All these areas and districts from above are grouped under 7 federal districts as follows: North-West, Central, Volga, South, Ural, Siberia and the Far East.
Each of these federal districts has their own capital but all of them are controlled by the central administration from Moscow.
The largest city in the country is Moscow, which is also the capital of the country with a total population of about 10 million people.
Population and language
Four-fifths of the country’s total population are ethnic Russians, but besides these, there are another 120 ethnic small groups that speak more than 100 languages.
Many of these ethnic groups are quite small, comprising just a few hundred people, while others are quite large with millions of members like Tatars, Ukrainians, Chechens, Armenians and Bashkir.
If we analyse this huge country from a language perspective, I can tell you that the official language is Russian spoken all over the country no matter where is Russia located in Europe.
Where is the Russia located in Europe and its huge dimensions impose the following split of the population from a linguistic perspective:
- Indo European group that is formed by East Slavic speakers and smaller numbers of other languages
- The Altaic group which includes Turkic, Manchu-Tungus and Mongolian
- The Uralic group made up of Finno- Ugric and Samoyedic
- The Caucasian Group that include Abkhazo- Adyghian and Nakhon- Dagestanian
As some of these ethnic groups are very small and in the Russian school everybody learns in Russian there are higher chances that in the future some of the local dialects spoken by people from certain parts of the country will disappear.
A short history of Russia
Now that we know where is Russia in Europe let’s discover the most important events that marked the history of this impressive country.
The part of Europe and Asia that today is the country of Russia had been inhabited by people for many years.
According to the historical evidence around year 800 the first Slavic people migrated into the area where Ukraine is today.
About 50 or 60 years later, King Rurik ruled the entire region from the city of Novgorod and the people who lived there were known as Rus.
A few years later, the people known as Rus conquered the city of Kyiv and put the basis of what was then known as the kingdom of Kievan Rus.
The newly formed empire became more and more powerful during the 10th and 11th century and during Vladimir the Great and Yaroslav I the Wise the empire became the most powerful empire from Europe.
During the next centuries, more exactly around the 13th century, the Mongols led by Batu Khan conquered the area and completely destroyed the Kievan Rus Empire.
Starting with the 14th century a new power rose in Europe and here I am talking about the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
The new power became the head of the Eastern Roman Empire and Ivan IV who is also known as Ivan the Terrible, the ruler of the new empire named himself the First Tsar of Russia in 1547.
The name Tsar is just a synonym for the name of Caesar as the Russians called their powerful Empire the “Third Rome” no matter where is Russia in Europe.
Another important moment in Russian history was in 1613 when Mikhail Romanov established the Romanov dynasty, one of the most important dynasties that ruled Russia for many years.
Under the rule of Tsar Peter the Great between 1689 and 1725, the Russian Empire continued its expansion and became a major power in Europe.
During its times, the capital of the empire was moved from Moscow to St. Petersburg, so don’t be surprised that St Petersburg is full of beautiful architecture and important monuments and a top attraction of where is Russia located in Europe.
During the 19th century, Russian culture was at its best and artists and writers like Dostoyevsky, Tolstoy and Tchaikovsky became famous all over the world.
Stay safe while you travel
- medical safety abroad
- medical assistance including COVID-19
- emergency medical evacuation
- trip interruption -up to $5.000
- travel delay - up to $100/day
But it seems that the luck is about to change for the Romanov family and Russian from all over the country fought against their leader, the Romanov Tsar after World War I.
The revolution was driven by the Bolshevik Party who was ruled by Vladimir Lenin.
In 1918 the revolution was over and a new chapter from Russia was about to start.
Vladimir Lenin’s party won the revolution and Russia became a communist state and by 1922 the Soviet Union was born.
Two years later, in 1924 Lenin died and Stalin took over the power.
The following years were marked by many executions and millions of people died in famines; it was one of the toughest periods from the latest Russian history.
On the horizon, the possibility of a new war appeared and in a few years, World War II started.
First, the Russians allied with the Germans but just a few months later, in 1941 the Germans invaded Russia.
More than 20 million Russians died in World War II including 2 million Jewish people who were killed as part of the Holocaust.
Not even World War II managed to change the boundaries of Russia even though where is Russia located in Europe makes it a very hot point on Europe’s map.
After the two World Wars were over, a new race began and here I am talking about the nuclear weapons race.
In 1949, the Soviet Union started to develop nuclear weapons competing with the United States in the so-called Cold War.
By 1991, the Soviet Union fell apart and many of the countries that formed it declared their independence.
The remaining areas that did not declare their independence became what today is known as the country of Russia or the Russian Federation.
Highlights of the most important historical events in Russian History
800– Slavic people moved from other parts of the world into the area known today as Ukraine
862– the area around the city of Novgorod was ruled by King Rurik and his people was known as Rus
882– the new king Oleg moved the capital city to Kiev
980– the newly formed kingdom known as Kievan Rus conquer new territories and expand its power
1015– a new king was named in the person of Yaroslav the Wise. During his reign, the kingdom reached its peak of power
1237– the kingdom was invaded by Mongols which destroyed almost everything they encounter, including cities, monuments and villages
1480– Ivan III managed to free Russia from the Mongols
1547– Ivan IV who is also known as Ivan the Terrible name himself the first Tsar of Russia
1552– the Russian empire stars its extension process conquering Kazan
1609– a new war starts when Poland invades Russia
1613– a legendary dynasty begins with the naming of Michael Romanov as Tsar. The Romanov dynasty ruled Russia for more than 300 years, until 1917
1654– Russia invades Poland and by 1667 a peace treaty is signed by both parties
1689– Russia has a new Tsar, Peter the Great, who put Russia on the world map as the most powerful country. All this was possible with many reforms adopted over the years and creating a powerful army
1703– the city of Saint Petersburg was created by Peter the Great and 10 years later, the city became the capital of the Russian Empire.
1725– Peter the Great dies and for the first time in medieval history a female runs the Empire and this is the wife of Peter the Great, Catherine I
1762– after the assassination of Tsar Peter III, his wife Catherine II took over the crown and ruled the empire for 34 years. This time was known as the Golden Age of the Russian Empire
1812– Napoleon invades Russia but his army was almost destroyed by the cold Russian winter. Three years later, in 1814 Napoleon and his army were defeated.
1853– the Crimean War begins which is in the end lost by Russia to an alliance of France, The Ottoman Empire, Britain and Sardinia
1867– Russia sells Alaska to the United States for 7.2 million dollars
1897– the Socialist Democratic Party was born. The party will be later divided into the Bolshevik and the Menshevik parties
1905– a Russian revolution starts and around 200 people are killed in a single day, known as the Bloody Sunday
1905– Tsar Nicholas II had to accept the October Manifesto according to which a parliament was born known as the Duma
1914– during World War I Russia fights on the side of Allies and it invades Germany
1917– the so-called October Revolution occurred and the communist Bolsheviks under Vladimir Lenin took control of the country.
1918– Russians exit World War I and give up Finland, Poland, Latvia, Estonia and Ukraine. In the same year, the Tsar Nicholas II family and himself had been executed by the Bolsheviks. The so-called Red Terror began as the country was now under the communist regime.
1922– the Civil war ended and the Soviet Union is established
1924– Lenin dies and the power is taken over by Stalin
1934– the great Stalin’s purge starts and more than 20 million people are killed
1939– World War II began and Russians invade Poland
1941– Russia is invaded by Germany and this forced Russia to joins the Allies
1942– the Russian army defeats Germany during the Battle of Stalingrad and released the country
1945– World War II ended and the Soviet Union controls a large part of the Eastern Europe including Poland and East Germany
1945– the Cold War begins
1949– The Soviet Union detonated an atomic bomb
1961– the first man in space is a Russian, Yuri Gagarin
1962– the Cuban Missile Crisis began as Russian places missiles in Cuba
1972– the US President Richard Nixon visits Russia
1985– Mikhail Gorbachev is elected as General Secretary and a new era begins for Russia. He institutes freedom of speech, the openness of the government and asks for economic reform.
1991– the Soviet Union fell apart and many countries gained their independence. Modern Russia was born
2000– Vladimir Putin is elected President
Conclusion
Where is Russia in Europe and its impressive size make it a unique country.
It is a very interesting mix of highly developed modern culture and many interesting and very well preserved national traditions deeply rooted in people.